- Differentiated energy: “KD Wood Powder”
- 1) Low cost fuel compared to conventional fossil fuel (diesel oil, LNG and petro cokes)
- 2) Zero carbon emissions; clean fuel with less pollution
- 3) Stable and even combustion quality

-

- With low moisture content (below 2%), calorific power is high and combustion efficiency is maximized, with increasing surface area of particles.
- Easy to keep due to low moisture absorption.
-

- No sulfur(S) and little ash.
- Usability of domestic forestry by-products can be increased.
-

- With full implementation of emission trading of greenhouse gases, emission trading can be ensured and a carbon management system is made possible when wood powder is used.
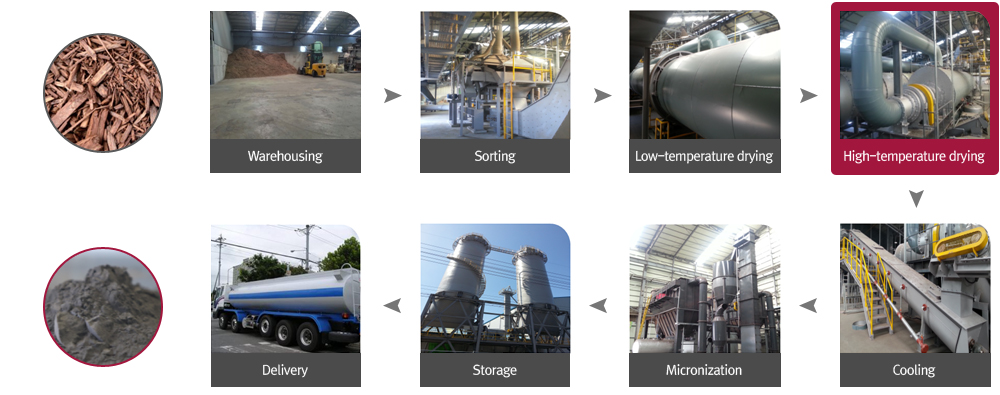
Manufacturing Process for KD Wood Powder
It is produced by applying self-developed high-temperature drying technology (condensing technology, waste heat recovery, and recombustion of dry distillation gas).
Korea’s first commercialization!
High-Temperature Drying Technology _ Division of Heat Treatment
Kyungdong Energy’s biomass heat treatment technology refers to the process carried out at below 200℃ (distillation) or 200~300℃ (torrefaction).
Division of heat treatment technology
- 1) Distillation (Post dry or Over dry)
- A process of applying heat sources to selectively remove a single component among polymers including moisture, hemicellulose, lignin, and cellulose - the main components that comprise biomass.
- 2) Torrefaction (Semi-Carbonization)
- A heat treatment process that dissolves most of the hemicellulose that comprises biomass; cellulose and lignin are not dissolved and are left. In this process, there is a tendency for the carbon content in the biomass to increase, while the hydrogen and oxygen content is reduced by removing combined water and hemicellulose.
- 3) Carbonization
- A chemical change that pyrolyzes many of the organic compounds that comprise biomass and concentrates and increases the carbon content.
| Carbonizing Temperature | Wood | Below 200℃ (Distillation) |
200~300℃ (Torrefaction) |
400~600℃ (Carbonization) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed carbon (%) | 13~14 | >20 | 20 ~ 50 | < 50 |
| Total carbon (%) | 51~52 | >55 | 55~70 | < 70 |
| Calorific power (kcal/kg) | 4300~4600 | 4800~5000 | 5000~6500 | < 6500 |
| Color | Deep Brown | Light Brown | Deep ~ Dark Brown | Black |
| Mass yield (%) | - | ~80 | 60~80 | < 40 |
Application of KD Wood Powder and Furnace Tests (Domestic)
Kyungdong Energy’s KD wood powder proved stable combustion quality and excellent economical efficiency, as proven by various field test!
-> Average 20~30% cost reduction compared to conventional fuel (bunker-C oil, LNG)
| Classification | Lime kiln | Industrial steam boiler | Aluminum melting furnace | General kiln | Drying furnace | Preheating zone of steelmaking ladle | Industrial steam boiler |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Name of company | P (Pohang) | S Mining Station (Samcheok) | D Metal (Gimhae) | R (Pohang) | D (Yeongwol) | P Steel Manufacture (China) | K (Yangsan) |
| Fuel | Pet-coke Bunker-C oil |
Bunker-C oil | Refined oil | LNG | Bunker-C oil | LNG | LNG |
| Production | High-grade quicklime | Hot water in the plant | AL Ingot | Zeolite diatomite |
Granular lime fertilizer | Stainless steel | Steam test |
| Production facility | BeckenBach Kiln | Steam boiler | Rotary reverberatory furnace | Rotary Kiln | Rotary Dryer | Steelmaking ladle | Steam boiler |
| Capacity of combustor | P. cokes combustor of the company | 1,000,000~ 4,000,000 kcal/hr (wood powder combustor) | 700,000~ 2,500,000 kcal/hr (wood powder combustor) | 2,500,000~ 3,500,000 kcal/h (wood powder combustor) | 2,300,000 kcal/hr (wood powder combustor) | 1,500,000 kcal/hr (wood powder combustor) | 2,500,000~ 3,000,000 kcal/h (wood powder combustor) |
| Cost reduction rate | Environmental advantage quality improvement (no sulfur) | Reduction rate 20~30% | Reduction rate 20~25% | Reduction rate~30% | Reduction rate 30~35% | Fuel supply with even cost reduction and calorific power | For combustion research |
- Kiln (furnace): Manufacture of fertilizer with high soil quality, cement, drying of agro-fishery products, quicklime manufacture, paper industry, incinerators
- Non-ferrous metals melting furnace: Aluminum melting furnace, non-ferrous metals (e.g. copper, tin, and lead)
- Steam boiler: Thermal power plant/textile/dyeing complex (community energy supply), petrochemical industry, paper, pharmaceuticals, residential convenience facility (building heating / hot water supply)
- Hot water boiler / hot-air blower: Greenhouse flowering
Examples of Overseas Applications of Wood Powder
In Europe, where greenhouse gas emission trading has been operating since 2005, conventional fossil fuel (oil/gas/charcoal) has been changed into wood powder fuel in and around local heating and wood processing plants. Wood powder fuel has been applied to commercial operations since the early 2000s.
[Application results of Swedish cooperator (wood powder burner and multi-fuel burner manufacturer)]
| Classification |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Finland | Sweden | Germany | Sweden | Thailand |
| Area applied | Local heating boiler | Wood pellet plant | MDF board plant | Hot water boiler (local heating) | Particle board plant |
| Date of commercial operation | 11.01.2013 | 10.01.2003 | 11.01.2001 | 11.01.2003 | 03.01.2003 |
| Capacity | 1 x 33 MW | 1 X 10 MW | 1 X 25 MW | 4 X 25 MW | 1 x 11 MW 1 x 5 MW |