Importance of Bio-Char
- 1) Response to climate change
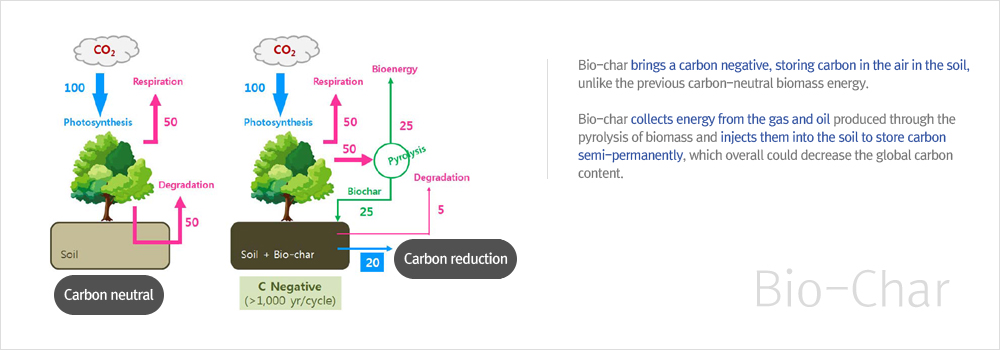
- Carbon dioxide in the air is fixed in the form of Bio-Char and returned to the soil, making the speed of the carbon cycle slow, controlling the emission of carbon dioxide for a long time, and reducing the emissions of methane and nitrous oxide, which have a bigger influence on climate change. (Using biomass as Bio-Char rather than energy could reduce the global carbon content by 20%.)
- 2) Energy production
- The gas (biogas) and the liquid (bio-oil) generated while producing Bio-Char can be used as energy sources. (Biogas in particular can be reused as an energy source for manufacturing Bio-Char.)
- 3) Improved agricultural productivity and soil enhancement
- Agricultural productivity is enhanced and damage to repeated cultivation is prevented by such features as neutralization of the pH of acidified soil, water-retaining ability, ion-exchanging ability, and offering a microbial residential area.
- 4) Waste management
- Deserted forestry and agricultural residues can be recycled.
Carbon Reduction of Bio-Char
- In 2010, in a nature communication thesis, Dr. Woof published a carbon reduction scenario:
- Bio-Char could cut down the global carbon content by about 20% (preparation and verification stage of carbon reduction certification).
- In 2013, the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) carried out a Bio-Char carbon isolation test:
- Flame grass farmland where Bio-Char was added emitted about 37% less greenhouse gas (max 55% less greenhouse gas was emitted in the lab condition) than land without it. Biochar
Overseas Examples of Bio-Char Effect
-

* 출처 : http://coolterra.com/
- Cool Planet Energy Systems (US)
- Results of a crop growth test showed that the output of cucumber, cabbage, and tomatoes increased by 40~56%.
-

* 출처 : http://www.carbongold.com
- Carbon Gold (UK)
- Use of irrigation water can be reduced by 30%.
-

* 출처 : http://seekfertilizer.com
- Seek Bio-Technology (China)
- Asparagus crop test: About 25% (25t/ha. vs 30t/ha.) increase in productivity compared to conventional fertilizer or compound fertilizer.
- Tulip crop test (Japan): 20~30% increase in productivity.